Kidney Cancer
Latest News
Latest Videos
CME Content
More News
Over 90% of patients in a phase 2 trial had at least some decrease in the size of target lesions.

Recent research has revived the controversy regarding the role of cytoreductive nephrectomy in this setting.

Rana R. McKay, MD, highlights developments with immunotherapy and targeted agents in the treatment paradigm for non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma.

Findings from the phase 3 KEYNOTE-581/CLEAR trial (Study 307) showed that the combination improved overall survival, progression-free survival, and response versus sunitinib.

"There is unmet medical need in trying to determine if there is a differential benefit to using one therapy over another in the non-clear cell setting," Thomas E. Hutson, DO, PharmD.

Among a small group of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who developed acute interstitial nephritis while on immune checkpoint therapy, 100% had a durable response to treatment.

At a median follow-up of over 2.5 years, the combination continued to show a significant benefit in overall and progression-free survival versus single-agent sunitinib.

Upfront nivolumab followed by response-dependent sequential use of ipilimumab did not optimize treatment outcomes in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.

The FDA is reviewing data from the phase 3 CheckMate-9ER trial, which showed that the combination significantly improved progression-free and overall survival compared with sunitinib in frontline renal cell carcinoma.

"Currently, there is significant variability in the design, conduct, and analysis of clinical trials for adjuvant treatment of both kidney cancer and bladder cancer. This variability negatively affects our ability to interpret trial results," said Richard Pazdur, MD.
The results may help guide treatment selection with immunotherapy versus targeted agents in patients with kidney cancer.
The combination significantly improved progression-free and overall survival compared with sunitinib in frontline renal cell carcinoma.

Investigators also reported that a subgroup of patients with 1 or more target kidney lesions experienced kidney tumor reduction and other benefits from the combination treatment.
“The combination of cabozantinib and atezolizumab demonstrated encouraging clinical activity in previously untreated patients with advanced ccRCC,” said investigator Sumanta Kumar Pal, MD.
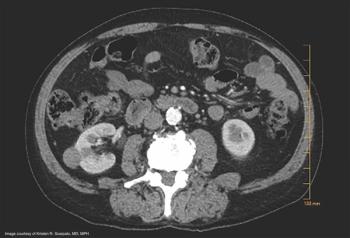
Renal mass biopsy should be used for patients in whom results would impact management decisions.

The combination improved overall survival versus sunitinib in patients with previously untreated advanced RCC.

Combination therapy is the first-line standard for metastatic renal cell carcinoma.

The novel HIF-2α inhibitor MK-6482 led to a decrease in the size of target lesions in almost 90% of patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease–associated renal cell carcinoma.
A study author said that “the long exposure [to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy] results in challenging surgery.”
“It’s case dependent. For appropriately selected patients, partial nephrectomy is preferred," says one urologist.
The phase 3 CONTACT-03 trial is exploring the combination of the multikinase inhibitor and immunotherapy agent in patients with renal cell carcinoma after exposure to an immune-checkpoint inhibitor.

Minimally invasive surgery was associated with similar overall survival and disease-specific survival outcomes compared with open surgery in patients with early-stage kidney cancer.

When compared with sorafenib, tivozanib showed improved progression-free survival, and a more manageable safety profile for patients with relapsed or refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma.

Dr. Kutikov discuss several noteworthy studies about kidney cancer from 2018.

"2018 was an exciting and productive year for kidney cancer research," write Amr A. Elbakry, MBBCh, MSc, and Ketan K. Badani, MD.